
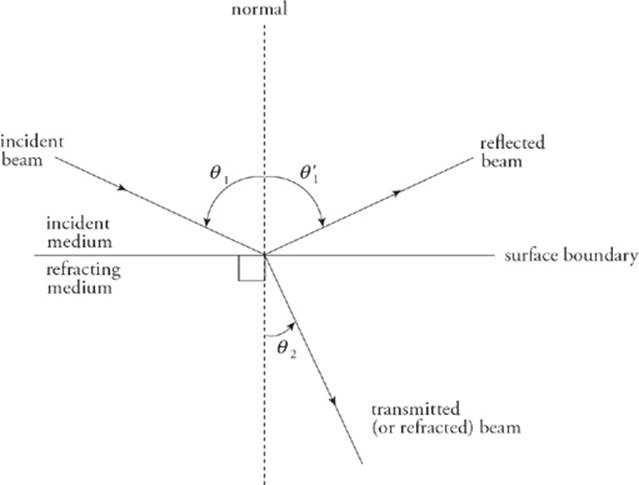
Step 2: Use Snell's law to define the relationship between n 1, n 2, θ 1 and θ 2 Θ 1 = angle of incidence (or incoming angle) = angle of reflection In the special case of a vacuum or air, n=1. However, it should be noted that the index of refraction for a given material is a function of wavelength and index increases as the wavelength gets shorter. All optical materials have a unique index of refraction that is a key characteristic of the material (ie: ZnSe, n=2.4). To Determine the answers to these questions, follow the steps below: Step 1: Define the variablesįind the index of refraction for both lower and higher mediums. What is the effect of polarization on the reflected and refracted portions of the incident light? What is the reflection loss of the incident light?ģ. What is the angle of refraction (θ 2) relative to the incident (θ 1) light? (It is generally known that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence).Ģ. There are three important considerations whenever this happens:ġ. Whenever an incident light traveling through one medium (ie: air with an index of refraction, denoted by "n", of 1) comes into contact with another medium with a high index of refraction (ie: glass with n=1.52), there is a reflected portion (bounces off the surface), and a refracted portion (transmits through the surface). We will also discuss two special cases, Brewster's Angle and the Critical Angle, which hae valuable applications in optics.

In this section, we will discuss some of the basic behaviors of light when it travels from one medium to another. Tech Notes » Reflection & Refraction of Light Tutorial


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
